What Are The Principles Of Biomimetic Design In Architecture?
Biomimetic architecture may sound like a complex term, but when you break it down, it's really quite simple. The term biomimetic refers to the design and construction of buildings that mimic the structures and functions found in the natural world. This approach is gaining popularity in the world of architecture, as it aims to create more sustainable and environmentally-friendly buildings.
Here are a few things you need to know about biomimetic architecture:
1. Concepts of Biomimetic Architecture
Biomimetic architecture is all about looking to nature for inspiration when designing buildings. Nature has perfected design over millions of years, and by studying it closely, architects can take cues from the natural world to create more efficient and sustainable buildings.
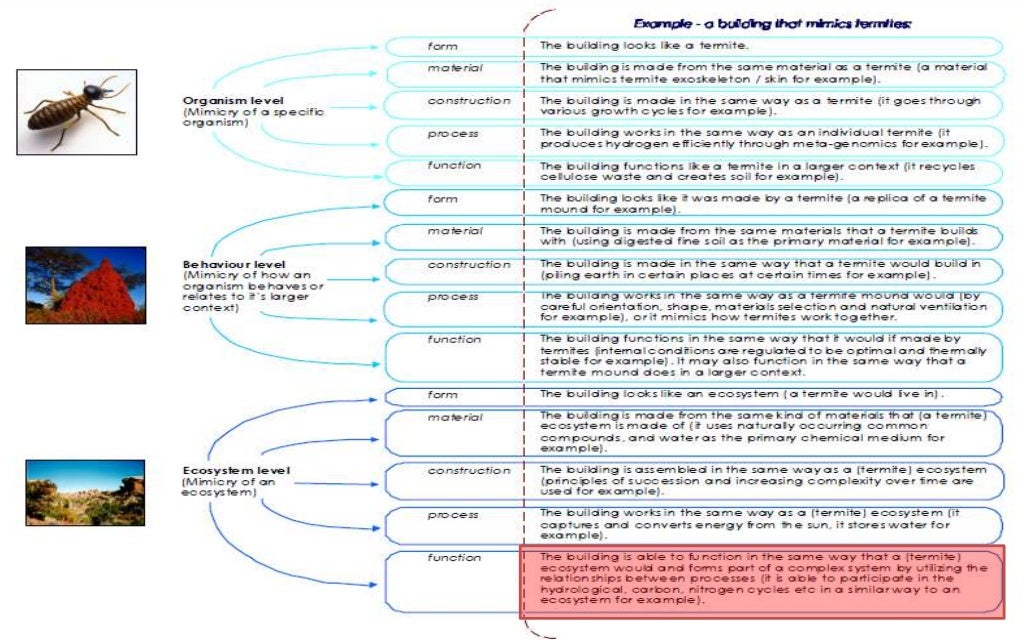
1.1. Bio-inspiration
The cornerstone of biomimetic architecture is bio-inspiration. This refers to the practice of observing and studying natural structures and processes in order to emulate them in the design and construction of buildings. Bio-inspiration involves looking at things like the way leaves capture sunlight, the way birds build their nests, and the way spider webs are structured.
1.2. Biomimicry
Biomimicry is another key concept in biomimetic architecture. It involves taking specific design elements or functionalities from nature and directly incorporating them into building design. For example, some buildings now feature walls that are covered in small bumps, mimicking the way shark skin reduces drag in water.
2. Benefits of Biomimetic Architecture
Biomimetic architecture offers a number of benefits over traditional building design. Here are just a few:
2.1. Sustainability
Biomimetic architecture is all about creating buildings that are more sustainable and environmentally-friendly. By looking to nature for inspiration, designers can create buildings that use less energy, materials, and resources. This can help reduce the environmental impact of buildings and make them more sustainable in the long-term.
2.2. Better Functionality
Many of the design elements found in nature are incredibly efficient and functional. By incorporating these elements into building design, architects can create buildings that are more functional, comfortable, and conducive to human well-being.
2.3. Unique Aesthetics
Buildings designed using biomimetic principles often have a unique and aesthetically-pleasing look. This is because they are inspired by the natural world, which has an inherently beautiful and harmonious design.
3. Examples of Biomimetic Architecture
Biomimetic architecture is still a relatively new field, but there are already some amazing examples of buildings that have been inspired by nature. Here are just a few:
3.1. Eastgate Centre in Zimbabwe
The Eastgate Centre in Zimbabwe is a commercial building that was inspired by termite mounds. The mounds are ventilated in a way that keeps the temperature inside constant, regardless of the temperature outside. The Eastgate Centre uses a similar ventilation system, which has helped reduce energy usage by up to 10% compared to traditional buildings.
3.2. Water Cube in Beijing
The Water Cube in Beijing was inspired by soap bubbles and created for the 2008 Summer Olympics. It features a unique design that captures and reflects natural light, making it a visually-stunning building both during the day and at night.
3.3. The Eden Project in Cornwall
The Eden Project in Cornwall features a series of interconnected domes that were inspired by soap bubbles and geodesic domes. The domes house plants and exhibits from around the world, and are designed to be energy self-sufficient, using only natural light and rainwater to sustain the plants.
4. FAQs
4.1. What is biomimetic architecture?
Biomimetic architecture is a design approach that takes inspiration from the natural world when creating buildings. It uses the structures and processes found in nature to create more sustainable and efficient buildings.
4.2. What are the benefits of biomimetic architecture?
Biomimetic architecture offers a number of benefits, including increased sustainability, better functionality, and unique aesthetics.
4.3. What are some examples of biomimetic architecture?
Examples of biomimetic architecture include the Eastgate Centre in Zimbabwe, the Water Cube in Beijing, and the Eden Project in Cornwall.
4.4. Why is biomimetic architecture important?
Biomimetic architecture is important because it offers a more sustainable and environmentally-friendly approach to building design. By looking to nature for inspiration, architects can create buildings that are more efficient, functional, and aesthetically-pleasing.
4.5. How can I incorporate biomimetic principles into my own building design?
If you are designing your own building, there are a number of ways you can incorporate biomimetic principles into your design. This could include using natural lighting, incorporating plants and greenery into your design, using recycled and sustainable materials, and designing for energy efficiency.
In conclusion, biomimetic architecture is an exciting and growing field that has the potential to revolutionize building design. By looking to the natural world for inspiration, architects can create buildings that are more sustainable, functional, and aesthetically-pleasing. If you're interested in learning more about biomimetic architecture, there are plenty of resources online to explore.



Post a Comment for "What Are The Principles Of Biomimetic Design In Architecture?"