How Does Architecture Incorporate Principles Of Universal Design?

Have you ever visited a building that was difficult to navigate because of narrow doorways or stairs? Or perhaps there was a park or public space that was not easily accessible for people with disabilities?
Universal Design Architecture seeks to alleviate these issues and make spaces more equitable and accessible for everyone. Here are some key points to know about this design philosophy:
What is Universal Design Architecture?
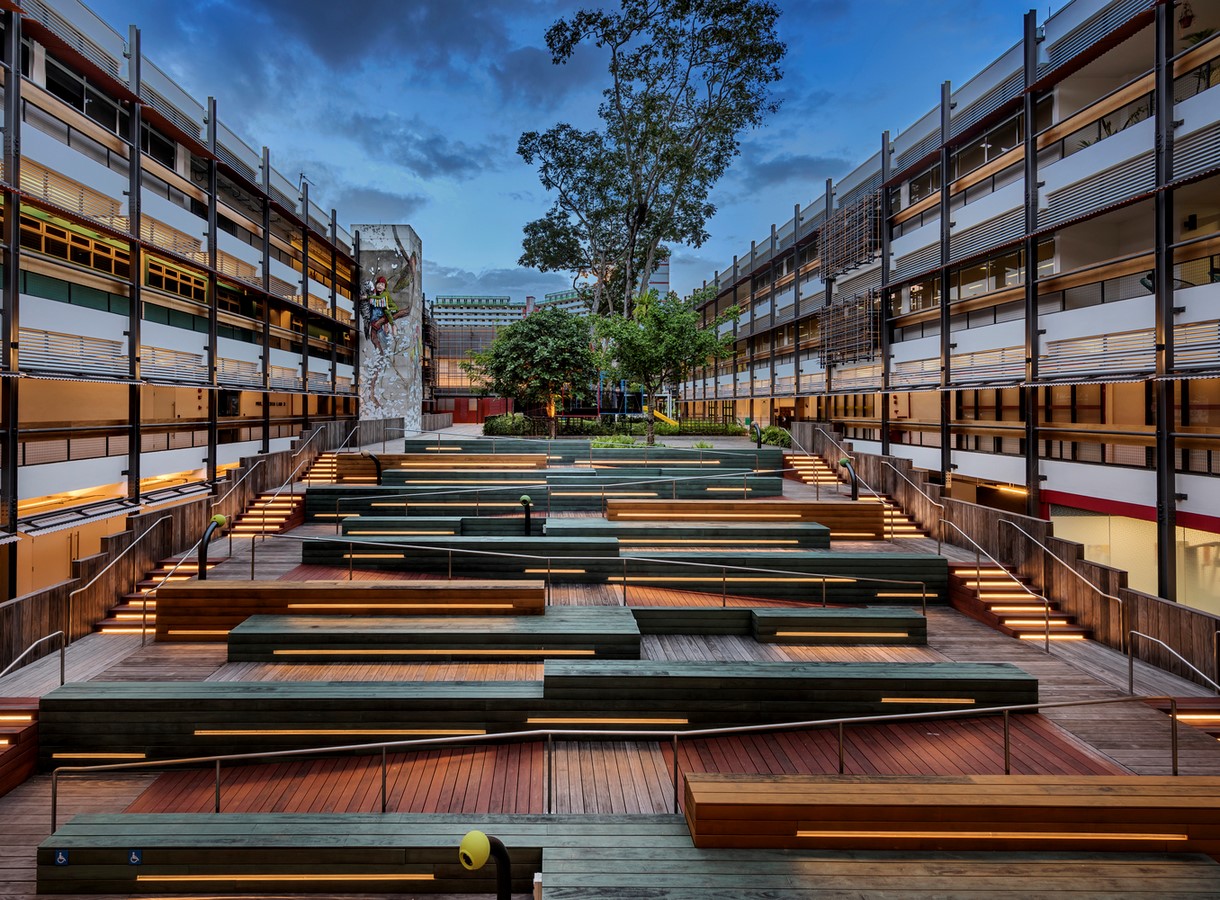
Universal Design Architecture (UDA) is an approach to design that aims to create spaces and products that are accessible and easy to use for people of all abilities. This includes people with disabilities, as well as children, older adults, and other diverse user groups.
UDA also aims to go beyond mere accessibility and create spaces that are aesthetically pleasing, functional, and adaptable to the needs of different people and situations.
Why is Universal Design Architecture important?
There are many reasons why UDA is important, including:
- Equity and inclusivity: UDA ensures that everyone has equal access to spaces and products, regardless of their abilities. It also promotes social inclusion and reduces stigma and discrimination against people with disabilities.
- Practicality and functionality: UDA creates spaces and products that are easy to use and adapt to different needs and situations. This can save time, money, and resources in the long run.
- Aesthetics and beauty: UDA recognizes that design is not just about function but also about form. By creating beautiful and well-designed spaces and products, UDA enhances the quality of life and well-being of everyone, regardless of their abilities.
How does Universal Design Architecture work?
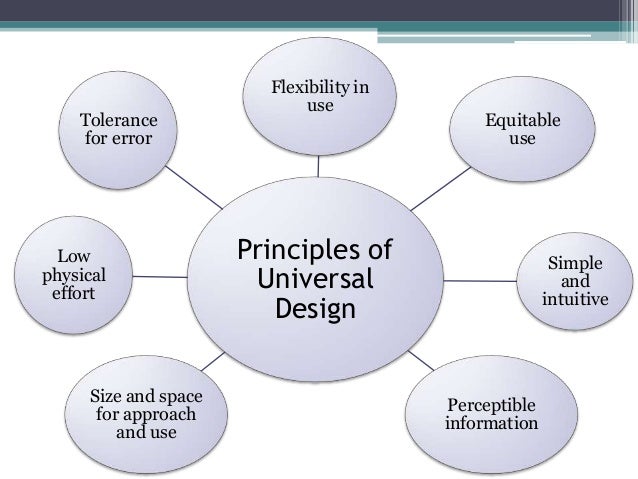
UDA works by following a set of guidelines and principles that ensure that spaces and products are accessible and easy to use for everyone. Some key principles of UDA include:
- Inclusivity: UDA seeks to include everyone in the design process and ensure that diverse user groups are represented. This can involve consulting with people with disabilities, older adults, children, and other user groups to understand their needs and preferences.
- Flexibility and adaptability: UDA creates spaces and products that can be easily adapted to different needs and situations. This can involve using adjustable or multi-functional furniture, or designing spaces that can be easily reconfigured.
- Simplicity and clarity: UDA aims to create spaces and products that are easy to understand and use, with clear signage, simple instructions, and intuitive layouts.
- Safety and durability: UDA ensures that spaces and products are safe and durable for everyone to use, with non-slip surfaces, easy-to-reach controls, and durable materials.
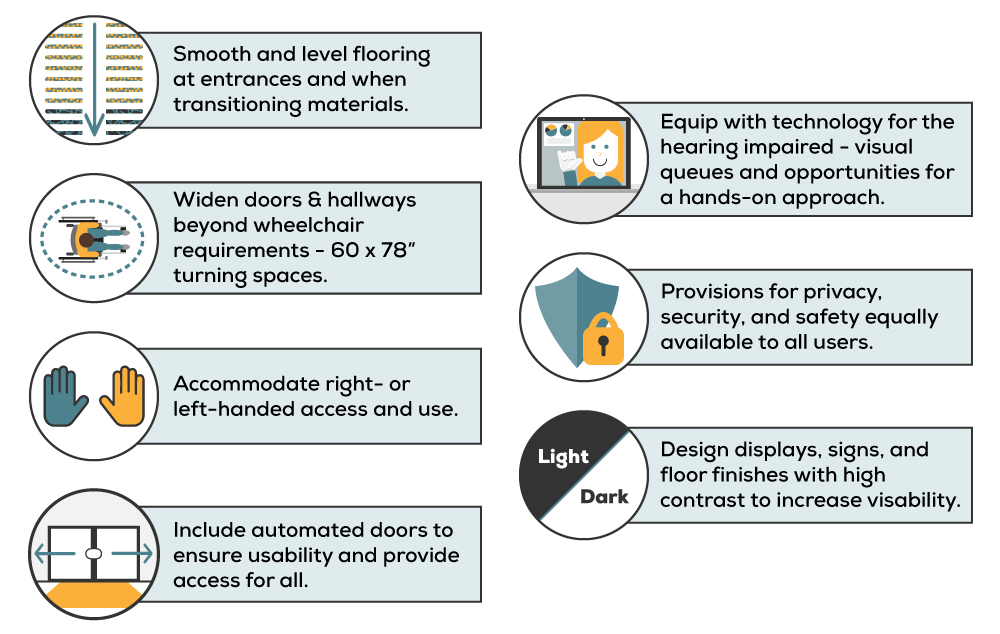
Examples of Universal Design Architecture
There are many examples of UDA in practice, including:
- Curb cuts: These small ramps at street corners make sidewalks and streets more accessible and easier to navigate for people with mobility impairments, as well as people with strollers, bicycles, or other wheeled devices.
- Accessible playgrounds: These playgrounds are designed to be accessible for children with disabilities, with features such as wheelchair ramps, sensory play equipment, and inclusive swings.
- Kitchen designs: UDA kitchen designs feature lower countertops, lever-style handles, and pull-out shelves to make them easier to use for people of all heights and abilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Universal Design and Accessibility?
Universal Design aims to create spaces and products that are accessible and easy to use for everyone, regardless of their abilities. Accessibility focuses specifically on making spaces and products accessible for people with disabilities, often through specific design features such as ramps or accessible bathrooms. While accessibility is an important aspect of Universal Design, Universal Design goes beyond mere accessibility and aims to create spaces that are inclusive, adaptable, and aesthetically pleasing for everyone.
Is Universal Design expensive?
While some Universal Design features may require more up-front investment, such as wider doorways or ramps, many Universal Design features can actually save money in the long run by reducing the need for expensive retrofitting or repairs. Additionally, Universal Design can increase the value and appeal of a property or product, making it a wise investment for the future.
Is Universal Design only relevant for people with disabilities?
No, Universal Design is relevant for everyone, regardless of their abilities. By creating spaces and products that are easy to use and adapt to different needs and situations, Universal Design benefits everyone, from children to older adults, to people with temporary injuries or illnesses. Universal Design also promotes equity, inclusivity, and social justice by ensuring that everyone has equal access to spaces and products.
What are some challenges of implementing Universal Design?
One challenge of implementing Universal Design is the lack of awareness and expertise among designers, builders, and policymakers. Many people may not be familiar with Universal Design principles or may not know how to implement them effectively. Additionally, there may be resistance or opposition to Universal Design from people who perceive it as an added expense or inconvenience. However, with education and awareness-raising, these challenges can be overcome, and Universal Design can become a mainstream and standard practice for design.
Where can I learn more about Universal Design Architecture?
There are many resources available for learning more about Universal Design, including books, online courses, and workshops. Some organizations that promote Universal Design include the Center for Universal Design at North Carolina State University, the Global Universal Design Commission, and the Universal Design Institute.
Universal Design Architecture has the potential to create spaces, products, and communities that are more equitable, accessible, and inclusive for everyone. By following the principles and guidelines of Universal Design, designers, builders, and policymakers can create a world that works for everyone, regardless of their abilities.


Post a Comment for "How Does Architecture Incorporate Principles Of Universal Design?"